Cross-Chain Swap Fees Explained: A 2026 Guide to Minimizing Costs
Why Cross-Chain Swap Fees Matter in 2026
Cross-chain swaps are now core to DeFi: users regularly move assets between ecosystems like Ethereum, Arbitrum, Base, Solana, and BNB Chain. Research cited in 2024–2025 bridge market reports shows cross-chain transaction volume jumping from about 18.6B to roughly 50B in just a few months and staying high into 2025.
With that growth, cross-chain swap fees have become a decisive factor for traders, yield farmers, NFT users, and professional on-chain participants. The “fee” you see in your wallet is only a small part of the real cost. To keep more of your capital, you need to understand the full fee stack and use tools that help you minimize it.

What Actually Makes Up a Cross-Chain Swap Fee?
A single cross-chain swap typically triggers multiple on-chain and off-chain actions. Each action adds cost, even when it isn’t labeled as a “fee” in your wallet.
Main components of cross-chain swap fees
| Component | Where it happens | What it covers | Visible to user? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source-chain gas | Origin network | Token approvals, DEX swap, bridge transaction | Yes (network fee line) |
| Destination-chain gas | Target network | Mint/unlock, optional DEX swap on destination | Sometimes (often implicit) |
| DEX / LP fees | AMMs / order-book DEXs | Pool fee (e.g., ~0.01–0.3%) baked into price | Indirect (in exchange rate) |
| Bridge protocol fees | Bridge smart contracts | Percentage fee, dynamic fee for pool imbalance / volatility | Often indirect |
| Aggregator routing fees | Cross-chain aggregators | Small protocol fee or spread on top of underlying routes | Usually indirect |
| Relayer / oracle fees | Messaging / intent systems | Payment to relayers and verifiers who move and attest transactions | Indirect |
| Slippage & MEV | Liquidity pools + mempools | Price impact of your trade size + MEV strategies like sandwiching | Implicit, not itemized |
Example: how costs can add up
The chart below shows an illustrative breakdown of a mid-sized cross-chain swap (around $2,000 notional) under moderate congestion. Numbers are approximate and for explanation only.
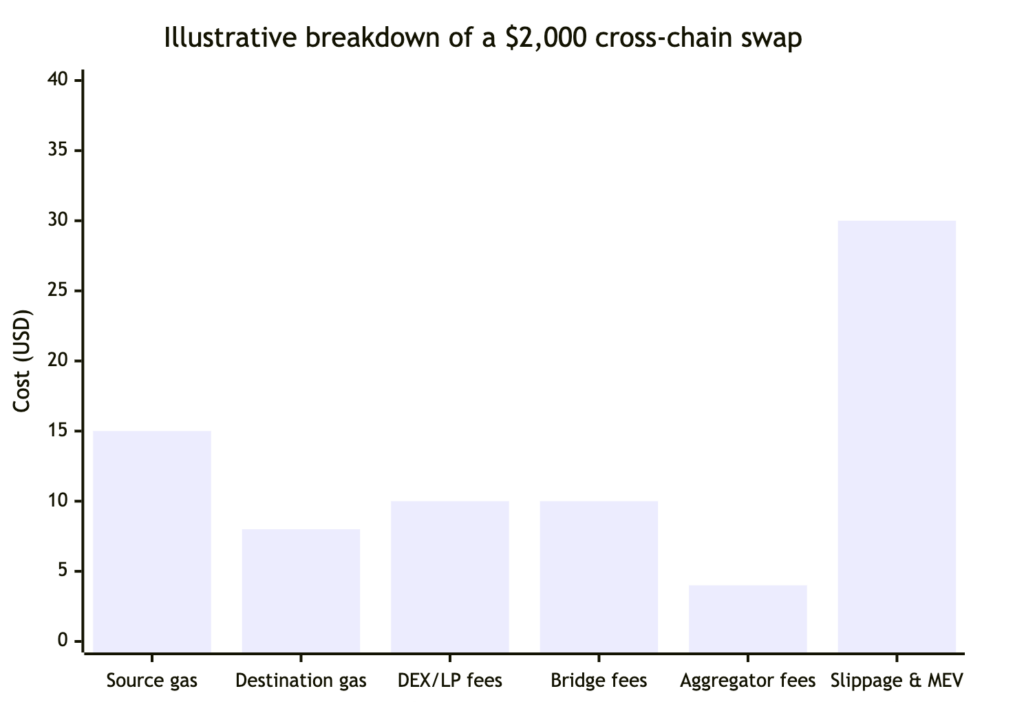
The key point: even if protocol and aggregator fees look small, gas plus slippage can easily become the biggest part of what you really pay.
Biggest Cost Traps Users Face (and How to Avoid Them)
Cross-chain users consistently run into the same cost pitfalls. Understanding these makes it much easier to minimize your cross-chain swap fees.
1. Opaque “all-in” cost
The most common complaint is: “I thought the fee was a few dollars, but the swap cost way more.” That happens because:
- You see source-chain gas but forget destination-chain gas.
- Bridge fees and DEX fees are buried in the quoted rate.
- Slippage and MEV quietly worsen your execution.
Practical fix: always think in terms of all-in cost:
- Source gas
- Destination gas
- Protocol/bridge + aggregator margin
- Difference between the mid-market price and what you actually receive (slippage)
2. Gas dominating small swaps
Studies of Uniswap v3 and similar DEXs show that for sub-$1,000 trades, gas can be over 90% of total cost on congested chains like Ethereum mainnet. Two common gotchas:
- First time using a token means paying for a separate approval transaction.
- Doing many small cross-chain moves instead of batching into one, when liquidity is deep enough, can multiply gas spend with little benefit.
Practical fix: for small amounts, prefer low-fee L2s and alternative L1s, and avoid unnecessary repeat approvals.
3. Slippage dominating large transfers
On large trades, price impact becomes the real fee:
- Your own trade moves the pool price against you.
- Thin liquidity or volatile tokens magnify this effect.
- MEV searchers can sandwich your trade, effectively increasing slippage.
Practical fix: on large moves:
- Check liquidity depth on both source and destination routes.
- Consider splitting the transfer into several chunks if the pool is shallow.
- Use routes and tools that reduce MEV exposure when available.
4. Double gas and surprise destination fees
Many users forget they’ll need:
- Native gas on the source chain to execute the swap/bridge.
- Native gas on the destination chain to finalize or use the received tokens.
Practical fix: before confirming, ensure you:
- Have enough native tokens for gas on both chains, or
- Use routes that handle destination gas efficiently via relayers where available.
How FoxWallet Helps You Minimize Cross-Chain Swap Fees
FoxWallet is built from the ground up as a multi-chain, non-custodial wallet with cross-chain operations at its core. That design directly targets the pain points above.
1. Non-custodial, security-first architecture
- You retain full control of your private keys; FoxWallet never holds user funds.
- Mnemonics and private keys are stored locally with encryption and sandbox isolation.
- Pre-transaction risk alerts and contract recognition help you avoid malicious or suspicious bridges and DApps that advertise “too-cheap” transfers.
This matters for fees because compromised or low-quality bridges often lure users with ultra-low costs before exploits occur.
2. Native multi-chain asset management
- One wallet for many chains, with automatic token and NFT detection.
- Unified cross-chain asset view with real-time on-chain synchronization.
That means you can see your balances and network conditions clearly across ecosystems, making it easier to decide when and where a cross-chain swap is actually worth the cost.
3. Built-in cross-chain and swap aggregation
FoxWallet integrates directly with leading on-chain liquidity and cross-chain infrastructure:
- A built-in DEX swap mechanism powered by a major aggregator (public reviews cite 1inch integration).
- A cross-chain bridge feature powered by LI.FI on the backend, as described in the FoxWallet Help Center:
https://hc.foxwallet.com/docs/basic/bridge
By delegating route selection to specialized aggregators, FoxWallet can:
- Search multiple bridges and DEX paths for better prices and lower LP fees.
- Automatically consider gas, pool depth, and protocol fees when building routes.
- Reduce hidden costs like unnecessary extra hops between chains.
4. Fee-awareness for every user level
FoxWallet is designed for:
- Beginners
- Clean UI with guided flows so you don’t have to understand every protocol under the hood.
- Key fee numbers surfaced before you confirm.
- Advanced and professional users
- Multi-chain and cross-chain operations from both mobile and browser extension.
- A consistent experience for frequent trades, advanced asset management, and deep DeFi usage.
For high-frequency or high-volume users, smaller improvements in slippage and route selection can translate into significant savings over hundreds or thousands of cross-chain swaps.
A Simple 5-Step Routine to Keep Your Cross-Chain Costs Low
You don’t need to be a protocol engineer to control your cross-chain swap fees. Build a simple routine around each transaction:
- Choose the right destination chain
- Prefer L2s or lower-fee L1s when they offer the DeFi apps you need.
- If you only need a stablecoin on another chain, don’t route through an unnecessarily expensive mainnet.
- Estimate your all-in cost before confirming
- In FoxWallet, review:
- Network fee on the source chain.
- Estimated fee impact on the destination chain.
- Expected output tokens.
- Ask yourself: “Does this total cost make sense relative to the amount I’m moving?”
- In FoxWallet, review:
- Use aggregator-powered routes, not manual hops
- Let FoxWallet’s integrated aggregators assemble routes instead of:
- Manually bridging to a chain.
- Then opening a separate DEX.
- Fewer steps often mean less gas, lower slippage, and fewer mistakes.
- Let FoxWallet’s integrated aggregators assemble routes instead of:
- Set sensible slippage tolerance
- For deep stablecoin pools, keep tolerance tight (e.g., around 0.1–0.5%).
- For more volatile tokens, use slightly wider settings but avoid extremely loose values that invite poor execution.
- Avoid peak congestion when possible
- If gas is spiking, consider waiting unless the move is time-critical.
- Use FoxWallet across multiple chains to route via cheaper networks where appropriate.
By combining these habits with a multi-chain, aggregator-native wallet like FoxWallet, you can significantly reduce both visible and hidden costs in your cross-chain activity.
If you’re ready to move assets across chains with more control over what you actually pay, explore FoxWallet on mobile or as a browser extension at:
- Main site: https://foxwallet.com
- Cross-chain bridge documentation: https://hc.foxwallet.com/docs/basic/bridge
